Plant protection measures for fruit trees in November
Author(s): ас. Кирил Кръстев, Институт по декоративни и лечебни растения – София
Date: 10.11.2025
862
Winter is already at the doorstep, and deciduous plant species are preparing for winter dormancy. After the leaves of fruit trees fall, it's time for important preventive plant protection measures. This will prevent an increase in phytopathogenic infection and insect population next year.
Now is also the time to prepare a plan for controlling diseases and pests next year, as well as to make a calculation of the preparations and materials needed to carry out the activities related to this control.
During the month, more suitable conditions for planting fruit trees and for carrying out phytosanitary activities on fruit crops will be available during the second ten-day period.

Since the mycelium of some diseases is preserved in leaves, fruits, and soil, and insects can overwinter in the soil, on mummified fruits and wood, and form caterpillar nests on shoots and leaves, the following measures are necessary:
For Pome, Stone, and Nut Fruits
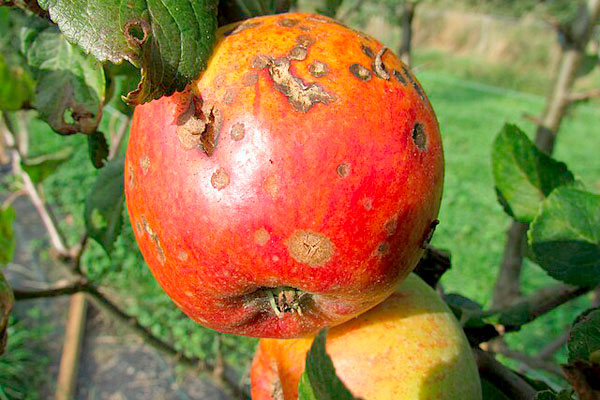

For apple and pear trees severely affected by scab and cherry trees by Cylindrosporium before leaf fall, their fallen leaves are collected and sprayed with 5% carbamide.
Peach, blackcurrant, sweet cherry, sour cherry, and almond plantations are sprayed with 2% Bordeaux mixture (2 kg bluestone and 1.5 kg quicklime per 100 L water) to combat shot hole disease and infectious apoplexy.
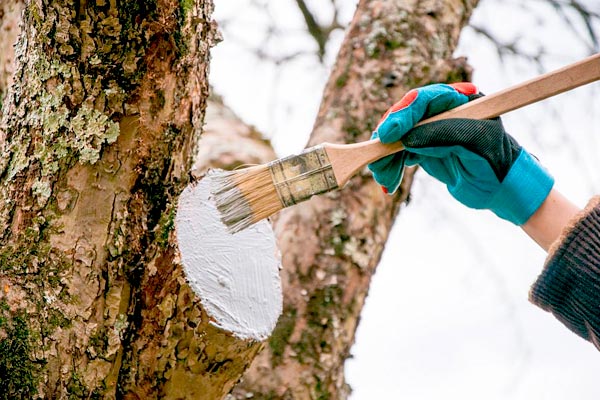

The trunks and thick branches of fruit trees are coated with 20% lime wash and a little clay to protect against winter frosts, to destroy lichens and mosses, and to repel the goat moth and leopard moth.
To combat brown and black rot, quince fruit drop, almond seed wasp, peach twig borer, brown-tail moth, and white ermine moth, mummified fruits and caterpillar nests are collected and destroyed.
Powdery mildew-infected shoots on apple and peach, scab, black rot, and brown leaf spot-infected shoots on pear, shot hole-attacked shoots on stone fruits and almond, brown rot-infected shoots on pome and stone fruit species, almond shoots attacked by cercosporosis, orange leaf spots, and scab, walnut shoots attacked by anthracnose and bacteriosis, hazelnut shoots attacked by hazelnut weevil, egg rings of the lackey moth, and egg shields of the apple moth are cut and burned.
To destroy the overwintering caterpillars of the codling moth, plum fruit moth, walnut fruit moth, pear bud weevil, apple leaf miner, bark tortrix moth, apple clearwing moth, pear psyllas, hawthorn mite, and egg masses of the gypsy moth, the old bark of fruit trees is scraped, collected, and burned.
Scraping is done with a blunt knife, without affecting the phloem part of the bark, and the waste is collected in a canvas and burned.
Fallen leaves in walnut plantations are collected and burned to destroy the overwintering anthracnose and bacteriosis infections within them.
The soil in fruit plantations is deeply plowed to destroy the apple sawfly, serpentine leaf miner, May beetle larvae, apple blossom weevil, pear bug, sour cherry leaf sawfly, cherry fruit fly, stone fruit sawfly, plum fruit sawfly, almond seed wasp, almond leaf sawfly, walnut fruit moth, hazelnut weevil, and chestnut weevil.
By deep plowing of the leaves, apple and pear scab, white leaf spots on pear, brown leaf spots on quince and pear, black rot on pome fruit species, quince fruit drop, red leaf spots on plum, cercosporosis, orange leaf spots and scab on almond, anthracnose and bacteriosis on walnut are also destroyed.
Thus, the leaves rot, and along with them, the pathogens die.
For Strawberries
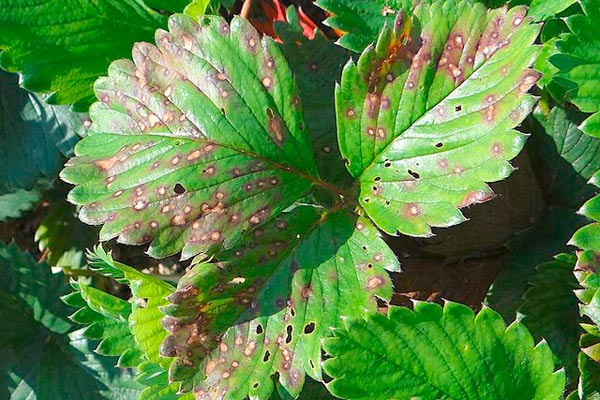

Strawberry white leaf spot is caused by a fungus that overwinters as mycelium in green leaves and as winter fruiting bodies in dried leaves. During winter, the fruiting bodies – perithecia – fill with many winter spores. With sufficient moisture and after completing their development, the spores are released into the air, thus causing primary infections. In the spots from primary infections, summer spores – conidiospores – are formed, which serve for the mass spread of the disease. The symptoms are most clearly expressed on the leaves – white round spots with a reddish periphery.
The soil is plowed to destroy adult strawberry stem weevils, strawberry weevils, white and red leaf spots.
For Raspberries
Anthracnose-infected, Didymella-infected, and raspberry gall midge or Agrilus-attacked shoots are cut and destroyed.
The soil between the rows of the plantations is plowed to destroy adult raspberry beetles and raspberry gall midge larvae, as well as the agents of rust, anthracnose, and leaf spots.
For Blackcurrants
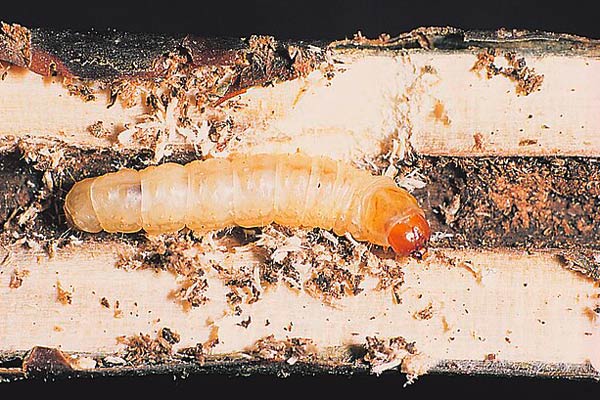
Blackcurrant clearwing moth larva
Shoots attacked by American powdery mildew and clearwing moth are cut and burned.
The soil is plowed to destroy the blackcurrant gall midge, which overwinters as a larva in a cocoon on the soil surface.

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/заглавна-защита-ноември.jpg)

