Аgricultural and technical activities in the orchard in April
Author(s): ас. Кирил Кръстев, Институт по декоративни и лечебни растения – София
Date: 07.04.2025
1262
April is expected to be characterized by unusually high temperatures and with a tendency for the expected average monthly temperature in our country to remain around and above the climatic norm, regardless of the forecast precipitation around and below the norm and lower temperature values during the first and at the beginning of the second ten-day period of the month. Late frosts in the high western fields and mountainous areas are also possible.
At the beginning of the month, snowfall is forecast in the Fore-Balkan and the mountainous areas. The average temperature in April will be between 13 and 22 oC in most regions, 13-15 oC along the Black Sea coast and between -3 and 5 oC in the mountains. The monthly amount of precipitation for the plains will be between 50 and 70 l/m2, and in the mountainous areas - between 80 and 100 l/m2. During the first ten-day period of the month (7-10 April) temperatures around 15-20 °C and more sunshine hours will be observed. Around 11-12 April a new cold spell will be observed, and between 11 and 15 April minimum temperatures down to minus 2-3°C are forecast, with an increased risk of damage to blossoms and young fruit set of fruit trees, and thunderstorms mainly over the mountainous areas, but temperatures will rise and the weather will be sunny until noon. The last spring frosts are expected at the end of the ten-day period. The expected maximum temperatures will be between 22-25 oC. By the end of the second ten-day period of April, the average monthly temperatures are expected to be around and above the climatic norm.
During the third ten-day period of April, high temperatures are expected, even values above 27-30 oC. In the first half of the third ten-day period, an increased probability of hail is forecast.
In fruit nurseries
Soil tillage is carried out in the seedbeds, mother plantations and nurseries. When the young shoots reach 20-25 cm, the first earthing up of the apple mother plants is carried out. The grafted walnut rootstocks earthed up in autumn are uncovered and the wild part is cut off about 0.5 cm above the grafted bud. All shoots emerging from the rootstock of the grafted plants planted in the nurseries are carefully removed. Delay in this practice hinders the development of the shoot from the cultivated bud. Often the competition from the shoots of the wild part is so strong that the bud does not sprout at all.
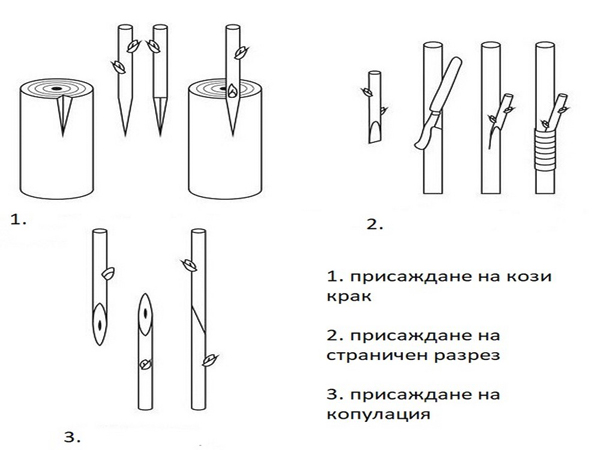
Work on grafting with scions on rootstocks with failed bud-grafts continues.
In fruit orchards
Work on planting new fruit orchards is being completed.

Work on filling in the places of failed trees in young orchards is being completed. In the absence of rainfall, all newly planted trees must be watered with 20-30 dm3 of water in the tree basin around the trunk.
The work on crown formation of the trees in the newly planted and young orchards is coming to an end. Shoots are removed from the trunk of the trees in the newly planted orchards. At a height of 50-60 cm above the soil surface, all shoots are removed. Thinning of part of the unnecessary shoots in the crowns of young trees is carried out. The shoots in young orchards are pinched out.
Pruning is carried out to weaken the growth of vigorous apple and pear trees. It is recommended for trees on seedling or vigorous vegetative rootstocks, trained as palmettes.
Re-grafting with scions in the crowns of mature trees continues.
Thinning of fruit set is carried out – in apples, some pear varieties and peaches.
How to protect fruit trees from freezing?
Measures are taken to protect plants from late frosts. The control consists of warming, smoking and air circulation, over-tree sprinkler irrigation or surface irrigation, and chemical products.
Warming of the air is achieved by burning high-energy combustible materials – fuel oil, diesel, natural gas, old car tyres. They are ignited one hour before the temperature drops to the critical point for the plants and the fire is maintained until one hour after sunrise.
For smoking, special smoke candles or inert materials such as straw, sawdust, branches, peat are used. They are arranged in small piles in the rows at 30-60 m from each other and at 5-6 m in the row. About 100 kg of combustible materials distributed in 10 piles are needed per 0.1 ha (decare).
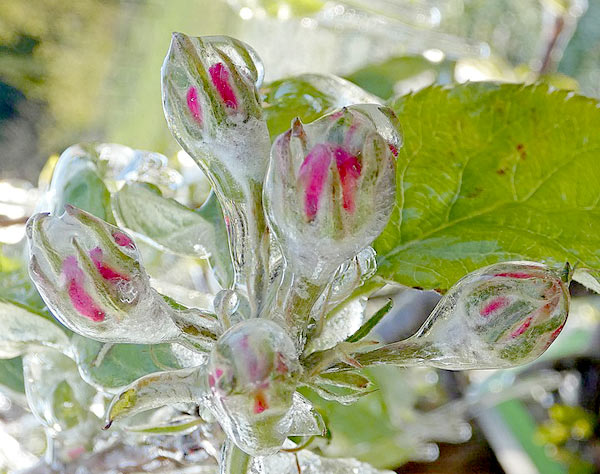

With over-tree sprinkler irrigation, the property of water to release heat when freezing is used, and by irrigating the orchards, the thermal conductivity and radiation of the soil are increased, as a result of which the air temperature rises by 2-3 oC.
To prevent crystallization of the cellular water in the buds and to protect against sub-zero temperatures, you can use products based on polymers and copolymers, such as Scudo Therm (1-2 l/100 l water) or another product.
Preventively or in case of freezing of flower buds and blossoms, to stimulate flowering, if the fruit species are still in this stage of development, they can be supplied with foliar application of a liquid fertilizer specialized for use during flowering - Cynoyl Z Special, ERT 23 plus, Archer OsmoCare or gibberellic acid.
In the plains and warmer regions, if the inter-rows are not being sown with ryegrass and white clover, a second, shallower soil tillage is carried out and, if not done in March, nitrogen fertilizer is applied.
In case of drought, irrigation is carried out. Soil moisture in the orchards during the flowering period and fruit set formation must not fall below 70% of field capacity.
Bee colonies are transported from already flowered orchards to those with intensive flowering.
In strawberry plantations
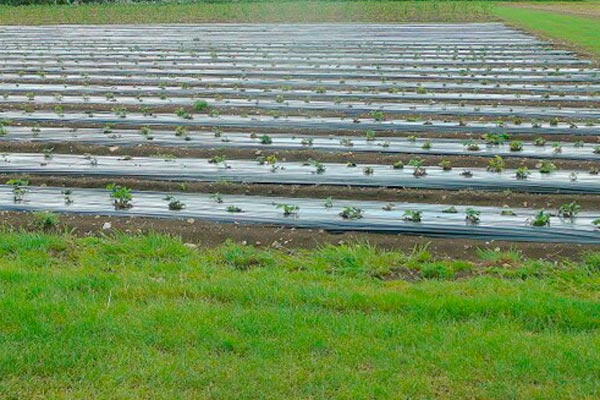

Filling in of the empty spaces in the areas planted in autumn (mainly in the higher regions) is being completed. Planting of virus-free strawberry planting material stored in cold rooms begins on beds covered with perforated black polyethylene.
The plants are planted so that the buds slightly protrude above the surface, without any risk that at the start of vegetation they will be covered by the polyethylene. Before planting, the roots of the seedlings are dipped in a slurry of farmyard manure, soil and water. If the roots are dried, their tips are cut off.
New strawberry areas planted on black polyethylene must be irrigated by sprinkler irrigation to ensure establishment.
Old plantations are tilled and, if they were not fertilized in March, fertilization is carried out beforehand. If necessary, the plantations are irrigated.
About 400-500 kg of straw per decare are transported for mulching the soil under the flower stalks and for protecting the fruits from contamination in plantations established without black polyethylene. Before that, the plantations are irrigated. The soil around the plants is covered with about 10 cm of straw. Mulching is carried out towards the end of mass flowering.
The soil in protected cultivation facilities is tilled and irrigated if necessary.
By mid-April, the last strawberry fruits are harvested from heated greenhouses. Harvesting of strawberry fruits from unheated (solar) greenhouses and tunnels begins. Later, field harvesting also starts. Greenhouses and tunnels are regularly ventilated. The required temperature is maintained in them for timely ripening of the fruits. In warmer sites and in plantations planted earlier, weeds that have emerged in the openings are weeded. Weeding is done very carefully so as not to pull out the not yet well-rooted plants.
In raspberry plantations

Filling in of empty spaces and planting of new areas is being completed. Soil tillage is carried out to keep the soil loose and weed-free and to incorporate the fertilizers. Towards the end of the month, top dressing is done with 10-12 kg of ammonium nitrate or the same amount of another nitrogen fertilizer. In case of drought, irrigation is carried out.
In blackcurrant plantations

Care is taken of the stoolbeds – tillage, fertilization and irrigation. New and old plantations are tilled and, if there is drought, irrigated.
In plantations with other crops
Planting of non-standard bay laurel plants in the nursery for further growing is carried out.
Spring budding of Caucasian persimmon with Japanese persimmon is carried out after the start of sap flow.
At the end of the month, pricking out of lemon seedlings in the open is carried out at 15-20 cm in the row and 1 m between rows.
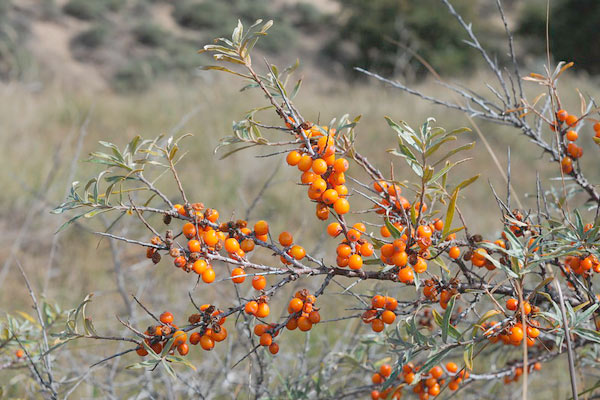

Depending on the needs, hoeing and irrigation of rooted cuttings of fig, pomegranate and sea buckthorn are carried out. Depending on the needs of the open field plot where rooting of cuttings of fig, pomegranate and sea buckthorn has been carried out, hoeing and irrigation are done. Planting of Japanese persimmon, sea buckthorn, pomegranate and fig in permanent sites continues.
Bay laurel trees are freed from their winter wrappings and winter protection. At the end of the month, the rooted plants of kiwifruit (Actinidia) from the previous year and the bay laurel saplings are transplanted to permanent sites. Newly planted plants are irrigated. The pricked-out seedlings of kiwifruit are planted in an open-field nursery. New sowing of bay laurel seeds in the open is carried out. Budding of pistachio rootstocks begins.

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/заглавна-овощна-агро-април-2025.jpg)

