Agrotechnical activities in the orchard in August
Author(s): ас. Кирил Кръстев, Институт по декоративни и лечебни растения – София
Date: 05.08.2024
1742
In August, shoot growth has been completed. The fruits of the autumn apple, pear and peach cultivars are enlarging intensively, and in parallel the process of differentiation of the fruit buds is taking place. The trees are being supplied with reserve nutrients.
The agrometeorological conditions during the month will be determined by temperatures around and above the climatic norms. A limiting factor for crop development during the month remains the deficit of soil moisture. The rainfall at the end of July was unevenly distributed and, in most of the country, belated and extremely insufficient to overcome the moisture deficit. In some of the western and southern regions, the soil moisture reserves in the 50 and 100 cm layers are completely depleted. Exceptions exist in certain places in Eastern Bulgaria, where at the end of July rainfall of over 30-40 l/m² (Razgrad, Shumen, Ruse, Burgas, Chirpan) was recorded, which moistened the upper soil layers.
During most days of August, the forecasted relatively dry weather will require the application of increased irrigation rates for the later fruit tree cultivars.
In fruit nurseries
Seedbeds are cultivated and irrigated.
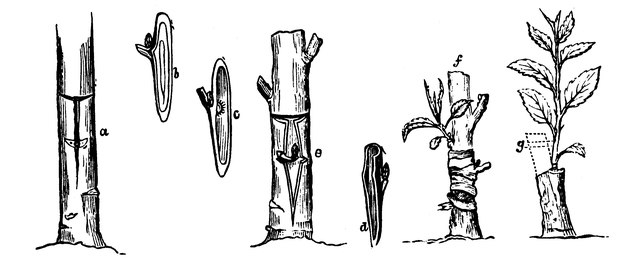
In first-year nursery beds, budding of the rootstocks continues
In second-year nursery beds, if necessary, the final disbudding of the rootstocks below the budding point is carried out.
Mother plantations are inspected and all off-types are uprooted. The gaps are promptly filled with plants of the main species.
Until the end of August, trees of apple, pear, peach and cherry can be grafted. During the second and third ten-day periods of the month, quince grafting begins.
The rootstocks budded in July are inspected and, where the union between scion and rootstock is good, the bindings are removed.
In fruit tree orchards
Soil moisture is monitored and irrigation is applied when necessary. After rain or irrigation, shallow soil cultivation is carried out to break the formed crust.
Mechanical weed control is carried out in the tree rows and in the inter-row spaces.
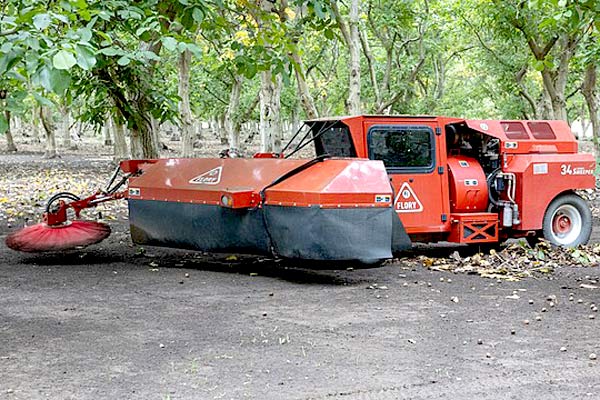

Walnut harvesting
Harvesting of peaches and of the early cultivars of apples, pears and plums continues. At the end of the month, the fruits of some early walnut cultivars are also harvested.
The necessary organizational work is carried out to prepare for the harvesting of the medium-early and late cultivars of apples, pears and plums.
Fruit storage facilities are disinfected and prepared for receiving the new production. Machines for sorting fruits are repaired and prepared for operation. Pre-planting preparation of the areas for establishing new orchards begins – deep ploughing, base fertilization and levelling.
In strawberry plantations
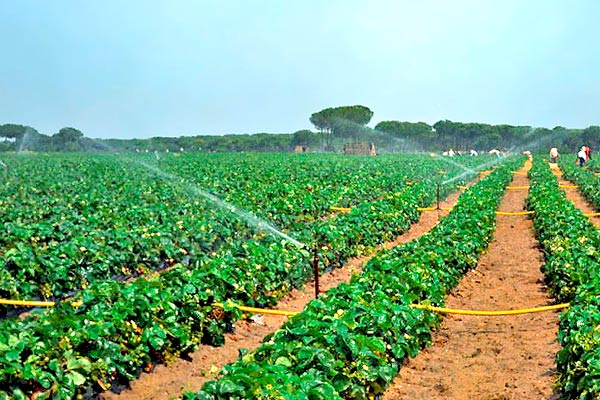

It is very important that all strawberry plantations are irrigated in a timely manner. Leaf desiccation must not be allowed. In August, the plants form the yield for the following year and an optimal water regime must be maintained. Depending on the age of the plantation and the soil type, 2-3 irrigations are carried out.
Runners are cut off from plants that are not intended for propagation material.
Care is taken of the mother plantations – weed control, irrigation and soil cultivation.
Preparation of new areas for autumn planting of strawberries continues. In some higher-altitude regions, planting may begin.
In raspberry plantations
Care for newly established plantations continues – irrigation is applied when needed and, if weeds are present, cultivation is carried out. Fruit-bearing plantations are irrigated so that the fruits can enlarge and flower buds for the next crop can be formed. Towards the end of the month, irrigation is stopped so that the new replacement canes can mature.
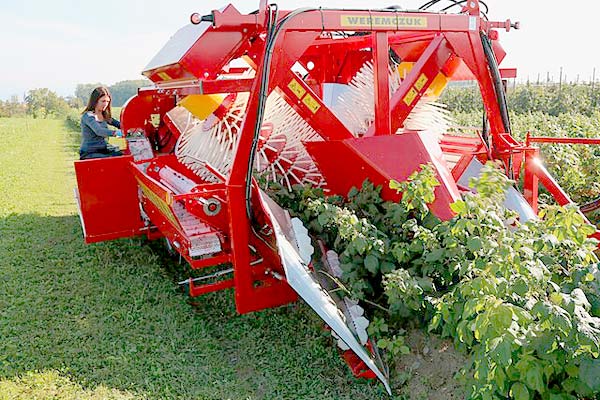

Raspberry harvesting continues
Care for the mother plantations continues – irrigation, top-dressing with nitrogen fertilizers and cultivation. By the end of August, irrigation is discontinued so that the canes can mature. And by the end of the month all fruited canes are cut, removed and burned.
Sites for the new plantations to be established in autumn are prepared. The soil is fertilized with 3-5 t of farmyard manure, 80-100 kg of superphosphate (or the same amount of another phosphorus-based fertilizer), 25-30 kg of potassium sulfate (or the same amount of another potassium-based fertilizer) per decare.
In blackcurrant plantations
Care for the rooting beds and young plantations continues. Soil drying and weed infestation are not allowed. In case of poor plant growth in rooting beds and young plantations, top-dressing is applied with 10-15 kg of ammonium nitrate (or the same amount of another nitrogen-based fertilizer) per decare.
Harvesting of fruits in higher-altitude sites is completed. Plantations are irrigated and cultivated regularly.
In plantations with other crops
Summer budding of rootstocks for persimmon, actinidia (kiwifruit), jujube and pistachio is carried out. 5-6 days before grafting, the nursery is irrigated abundantly for better bark slipping. 3-5 days before budding, scions are collected and kept in the shade in a cool room. The take of the budded persimmon plants and others is checked.
Lemon is budded with a dormant bud. Lemon seedlings are abundantly irrigated one week before grafting and immediately after it.
Marking of the desired cultivars and forms of fig, sea buckthorn and chokeberry continues, as well as rooting of green cuttings of actinidia, chokeberry, sea buckthorn and pomegranate.
Care for irrigation and hoeing of plantations with southern crops continues, with particular attention paid to newly established plantations.
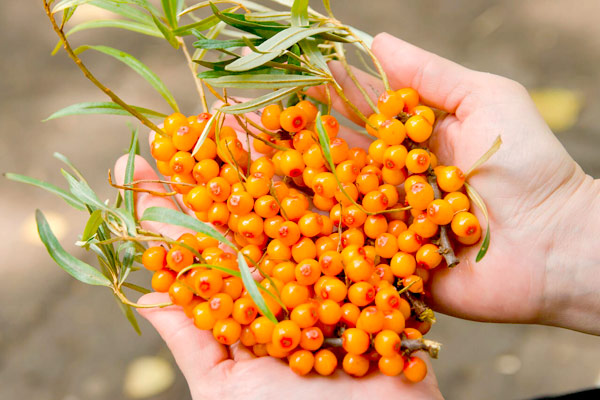

Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides), also known as rakitnik, Siberian pineapple or sea buckthorn, is a species of flowering plant from the family Elaeagnaceae. The plant has a very well-developed root system that holds the soil on steep slopes. The roots maintain a symbiotic relationship with actinomycetes. This relationship allows nitrogen to be fixed from the air. They also transform the insoluble organic and mineral resources in the soil into soluble forms.

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/заглавна-агро-август.jpg)

