Digital catalogue of the plant gene pool in Bulgaria
Author(s): доц. д-р Николая Велчева, ИРГР Садово
Date: 13.03.2024
1542
In recent years, the importance of the plant gene pool for the prosperity of breeding, agriculture and ecology has been increasingly recognized. Plant genetic resources are a factor that contributes to limiting ecological erosion and are a source of useful traits for adapting crops to the growing negative impact of climate change.
The Institute in Sadovo, part of the Agricultural Academy, is the successor of a rich history and traditions in agricultural science. The Institute of Plant Genetic Resources (IPGR) is the National Coordinator of all activities related to the conservation and management of plant genetic resources (PGR) in Bulgaria and represents our country in the European Cooperative Programme for PGR (ECPGR) https://www.ecpgr.cgiar.org/.

The main tasks of the research process are: enrichment with new PGR accessions; characterization and evaluation of PGR according to international descriptors; maintenance of PGR; storage in a gene bank under controlled conditions; documentation of PGR; use of the plant gene pool in breeding and practice.
Stages of development of plant genetic resources documentation at IPGR-Sadovo:
Stage I: Before 1982 – Field notebooks; lack of digitization.
Stage II: 1982-2000 – Information and Documentation Centre – paper data and an electronic database on a single computer; documentation in separate files; passport data according to a harmonized international descriptor; characterization and evaluation information according to UPOV classifiers.
Stage III: 2000-2021 – Phyto 2000 electronic catalogue in MS Access format – passport database; characterization and evaluation information according to UPOV classifiers, IBPGR and ECPGR descriptors in MS Excel.
The Phyto 2000 electronic database is of the “registry” type and contains the following sets of passport data:
- taxonomic description
- accession number
- date of registration
- country of origin
- donor of the accession
- ecological and geographical characteristics of the area of origin
- biological status
The accession number provides identification of the accession at the different storage levels: long-term, medium-term, short-term, in vitro and/or field collection, in a botanical garden.
Stage VI: Since 2021 – Development and integration of an Intelligent Information System for the management of ex situ collections.
Information system for documentation of plant genetic resources
In the period 2021-2023, under the BGPLANTNET project funded by the National Science Fund, an intelligent information system “Genebank” was developed for managing the documentation of plant genetic resources in Bulgaria http://delc.space/genbank/. A relational database has been implemented and a large part of the data from Phyto 2000 has been migrated into it through scripts created for this purpose.
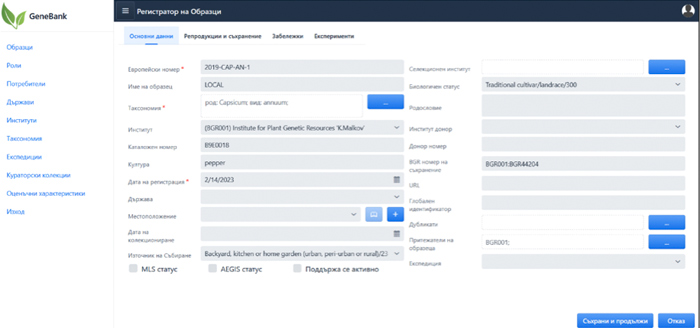
A system for storage and management of plant genetic resources – GenBankSystem – and a modern interface have been developed. The system enables exports for automatic data transfer to international plant genetic resources systems.
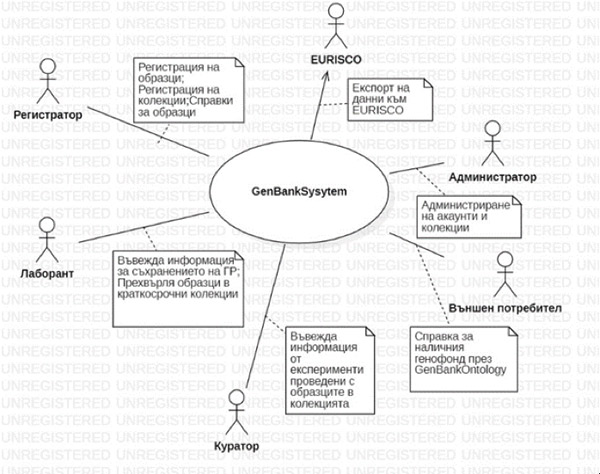
Status of the National Plant Genetic Resources Collection (1982-2024)
The existing gene pool is enriched annually, its conservation is monitored and it is provided to national and international research centres. The expansion of the genetic base of the collections is achieved through expeditions to specific regions, in accordance with the tasks of ongoing projects, and through international non-monetary exchange.
- Taxonomic descriptions: 3,723
- Number of registered: 54,175 accessions
- Botanical families: 122
- Local varieties and populations: 11,063 accessions
- Varieties and breeding lines: 6,221 accessions
- Introduced through international non-monetary exchange: 36,891 accessions
- Foreign partners: 203
The collection maintained in the National Genebank is represented by germplasm diverse in botanical composition and biological status. It includes wild relatives, local accessions and primitive varieties, as well as breeding lines and varieties developed to meet specific economic criteria. The collection includes accessions of cereal crops (62%), grain legumes (16%), forage (3%), industrial (8%), vegetable crops (10%) and 1% are medicinal and ornamental plants. The database has been converted into the format of the FAO/Bioversity International (2017) International PGR Documentation Standard.
International information networks for plant genetic resources
The National Genebank has been nominated as the focal point for Bulgaria in the European PGR Catalogue – EURISCO (http://eurisco.ecpgr.org/). Through EURISCO, information on the PGR collection is publicly available in other international databases such as AEGIS, FAO WIEWS, GENESYS, etc. The Bulgarian PGR collection is the seventh largest national collection in Europe with 70,834 acc., distributed in 532 genera and 1,927 plant species. The genera characterized by the largest number of accessions are: Triticum, Hordeum, Zea, Phaseolus, Avena, Capsicum, Pisum, Arachis.
Safety duplication of the Bulgarian PGR collection
The Memorandum of Cooperation between IPGR-Sadovo and the Centre for Genetic Resources in Wageningen, the Netherlands was signed in 2008 and 762 accessions of 4 crops (melons, pumpkins, cucumbers, watermelons) were sent for safety duplication in their genebank.
Pursuant to an agreement between IPGR-Sadovo and the Ministry of Agriculture and Food of the Kingdom of Norway, signed in 2014, 2,119 local Bulgarian accessions were sent for safety duplication to the Svalbard Global Seed Vault:
- 2014 – 933 accessions (bread wheat, durum wheat, barley, maize, sorghum, rye, oats, common bean, chickpea, lentil, faba bean, pea, grass pea and lettuce);
- 2022 – 1,186 accessions of 32 plant species.
Conservation of local plant gene pool
Bulgaria is a traditional producer of a wide variety of agricultural crops, characterized by very good taste and high biological value of the produce. Tomatoes, pepper, common bean and many other vegetables and pulses are widely represented in our national cuisine and in the dishes of the Balkan countries. Expeditions are carried out in different geographical regions of the country and valuable local varieties, populations and wild relatives are collected. Developed as a result of long-term selection within populations for valuable traits and qualities, and adapted to the specific conditions of the area where they are grown, local varieties are a unique initial material for breeding under climate change conditions and for restoring the traditional taste in practice.

Digital catalogue of local plant genetic resources
Under the National Research Programme “Healthy Foods for a Strong Bioeconomy and Quality of Life” of the Ministry of Education and Science, an electronic platform for local PGR has been created (https://plantsdigcatalog.agriacad.bg/). The digital catalogue includes passport data and characterization information for local accessions of crops of economic importance and traditional for Bulgaria: maize, common bean, cowpea, chickpea, faba bean, pepper, tomatoes, eggplant, cucurbits, garlic, medicinal and ornamental species.
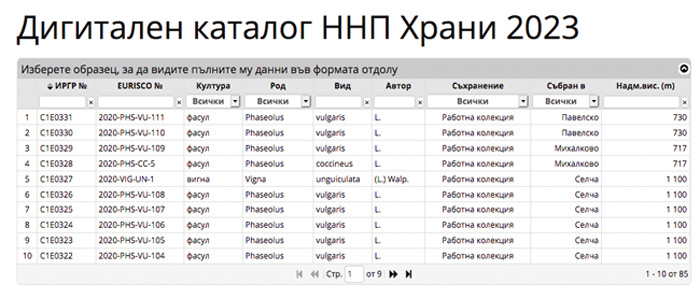
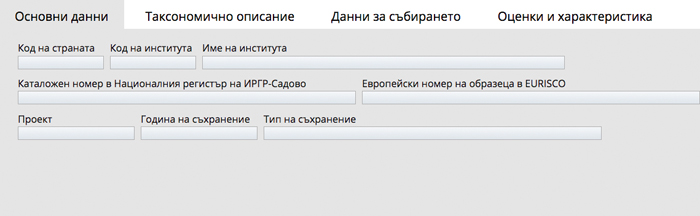
Future priorities for improving the work on plant genetic resources documentation are:
- Optimizing, improving the quality and efficiency of the genebank documentation system and using PGR information in interoperability with international standards for plant gene pool conservation.
- Enriching existing collections with local PGR and wild relatives of cultivated plants for their sustainable conservation.
- Free distribution, exchange and use of the national gene pool in breeding and the reintroduction of traditional crops and varieties into practice.
- Strengthening cooperation and building research networks in the field of PGR through new projects and with various stakeholders at international, national and regional level.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the Science Research Fund of the Ministry of Education and Science under the project “Bioactive substances from legume and medicinal species – characteristics and potential for use under changing climate conditions” (KP-06-N56 /13/ 19.11.2021).

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/дигитален-каталог-заглавна.jpg)

