In the orchard in March – time for pre-bloom sprays
Author(s): ас. Кирил Кръстев, Институт по декоративни и лечебни растения – София
Date: 08.03.2024
2295
During the first days of the first ten-day period of March, temperatures are forecast to be above the climatic norms. By the end of the period, temperatures are expected to decrease to values close to the climatic norms.
During the second and third ten-day periods of March, agrometeorological conditions will be determined by dynamic weather. In fruit crops, different phenological stages will be observed, from bud swelling and bud break to pink bud and beginning of flowering in early-flowering species – apricot, peach, almond. In March, the forecast minimum temperatures down to minus 5°C, depending on the duration of exposure, will pose a risk to advanced fruit crops in the stages of bud formation and flowering.
Precipitation is expected at the end of the first, in the middle of the second ten-day period and at the end of the month, which will increase soil moisture reserves in the one-metre soil layer.
More favourable conditions for carrying out pre-bloom plant protection sprayings in orchards against early brown rot, shot-hole disease, peach leaf curl, and scab in pome fruit will occur during the first half of the first ten-day period, at the beginning and at the end of the second one.
Agrotechnical activities
In fruit nurseries
Sowing in seedbeds and planting of rootstocks in the nursery are completed. Mother plantations are planted no later than the end of the first ten-day period. Two-year-old mother plantations are pruned to a stub – 3-4 cm above the soil surface.
Seedbeds with pome fruit species, mother plantations and second-year nurseries are fertilised with 10-12 kg/da ammonium nitrate or with the equivalent amount (corresponding to 10-12 kg/da ammonium nitrate) of another nitrogen fertiliser.
Seedbeds are cultivated to break the soil crust, destroy weeds and incorporate the nitrogen fertiliser.
If necessary, thinning of rootstock material is carried out. Plants of pome fruit species are left at a distance of 6-8 cm, and of stone fruit species – about 4 cm from each other.
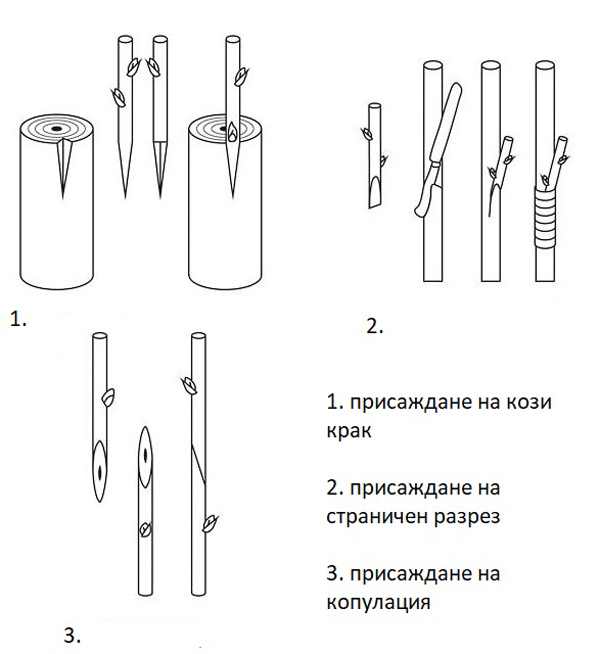
Un-grafted rootstocks in the nurseries are regrafted with scions. In practice, regrafting is most often done by cleft grafting, side grafting or whip-and-tongue grafting (copulation).
In orchards
Until bud break, pruning for production and rejuvenation of pome and stone fruit species and for crown formation in young plantations can be carried out.
New orchards are planted, and at the same time the first pruning is carried out. Filling in the gaps of dead trees in young plantations continues.

The first top dressing with nitrogen fertilisers is carried out. In young plantations, only the tree rows are fertilised, and in old plantations – the entire inter-row space. The fertiliser is broadcast on the surface and incorporated by shallow soil cultivation. The required fertiliser rates are determined according to the results of leaf analysis carried out in the previous year. If no analysis is available, fertilisation is done with 15-20 kg/da ammonium nitrate or with the same amount of another nitrogen fertiliser.
Bee colonies are provided for flower pollination. For 10 da, 3-4 sufficiently strong bee colonies are ensured. It is most appropriate to place them on both sides of the rows. Bees achieve maximum pollinating capacity in sunny and calm days with temperatures of 20 – 22 oC, when they can move up to 3 km away from the hive.
Measures are taken to protect plants from late frosts. Control measures consist of heating, smoking and air movement, sprinkler irrigation or flooding, and chemical preparations. Air heating is achieved by burning high-energy combustible materials – fuel oil, diesel, natural gas, old car tyres. They are ignited one hour before the temperature falls to the critical point for the plants and the fire is maintained for one hour after sunrise.
Special smoke bombs or inert materials such as straw, sawdust, branches, peat are used for smoking. They are arranged in small heaps in the rows at 30-60 m from each other and 5-6 m within the row. About 100 kg of combustible materials distributed in 10 heaps are needed per 1 da.
In sprinkler irrigation, the property of water to release heat when freezing is used, and through irrigation of the plantations the thermal conductivity and radiation of the soil are increased, resulting in a rise in air temperature by 2-3 oC.
To prevent crystallisation of cell water in the buds and protect against sub-zero temperatures, preparations based on polymers and copolymers such as Scudo Therm (1-2 l/100 l water) or other products may be used.
Frost cracks are treated by nailing with small nails. Longitudinal frost cracks are coated with tree wound dressing.
If necessary, irrigation is carried out before or during flowering. It is usually required when winter is dry, followed by a spring with insufficient rainfall.
Old trees and trees of low-value cultivars are regrafted.
The scaffold branches are usually shortened just above the second-order scaffold branches, and the leader – slightly above the level of the scaffold branches. Thicker scaffold branches are used for regrafting, and are shortened depending on their position – the lower ones are left longer, and the higher ones – shorter. Very good results are obtained when cleft grafting is used.
In strawberry plantations

Filling in new places with strawberries
Empty spaces in new strawberry and fruit-bearing plantations are filled in.
Fertilisation is done with 10-12 kg/da ammonium nitrate or with the same amount of another nitrogen fertiliser, followed by hoeing. In dry conditions, irrigation is carried out.
In heated greenhouses, when the fruits begin to ripen, soil temperature is raised to 15-18 oC, and air temperature – to 20-25 oC. Greenhouses are ventilated during the warm hours of the day. To ensure good pollination in greenhouses, 2-3 bee colonies per 10 da are introduced.
In raspberry plantations
Filling in of empty spaces in plantations continues.

If not cut after harvest, last year’s fruiting canes are cut and burned
In two-year-old plantations, all weak root suckers are cut at soil level, leaving 2-3 of the strongest to form the bushes.
In older plantations, pruning for shortening is carried out. Replacement canes are also thinned.
Plantations are top-dressed with 10-12 kg/da ammonium nitrate or with the same amount of another nitrogen fertiliser and are hoed.
If autumn fertilisation with farmyard manure and phosphorus and potassium fertilisers has not been carried out, it is done now. Apply 50-60 kg ordinary superphosphate or 25-30 kg double superphosphate, 15-20 kg potassium sulphate – or the same amount of other phosphorus and potassium fertilisers and 2-3 t well-rotted farmyard manure per decare. Fertilisers are ploughed in, requiring deeper tillage.
In dry conditions, irrigation is applied.
In blackcurrant plantations
Planting of stored blackcurrant cuttings in the rooting bed continues.
Top dressing with 10-12 kg/da ammonium nitrate or with the same amount of another nitrogen fertiliser and shallow cultivation is carried out.
Last year’s rooting beds are cultivated.
In dry conditions, irrigation is carried out.
In plantations with other crops
Seeds of Caucasian persimmon are sown in the nursery. In-row spacing is 5 cm with 80 cm between rows, and sowing depth – 3 – 4 cm.
Cuttings from fig, pomegranate and sea buckthorn are collected.
Cuttings of fig, pomegranate and sea buckthorn are planted outdoors.
With in-row spacing of 10-15 cm and 80-100 cm between rows.
The soil around the cuttings is firmly pressed, after which they are covered 1-2 cm above the terminal bud. Immediately after planting, abundant irrigation is carried out.
On grown rootstocks of Caucasian persimmon, scion grafting with persimmon (kaki) is carried out.
Planting of trees of persimmon, sea buckthorn, pomegranate not planted in autumn continues.
Pruning for formation and production in pomegranate is carried out.
Lemon seeds are planted outdoors in beds at spacing 20 x 5 cm. The soil should be loose, enriched with well-rotted farmyard manure.
Plant protection activities
In fruit nurseries
Before planting seedlings and cuttings in mother plantations and first-year nurseries, for control of soil pests, treatment is carried out with Ercole GR (1-1.5 kg/da), Trika Expert (1-1.5 kg/da) locally, only in the planting furrow, near the plant roots. Against soil pathogens – root rots, bacterial crown gall – roots are dipped in a solution of a fungicide with active ingredient copper oxychloride – Capper Key, Kodimur 50 WP, Kuprocin 35 WP (18-30 g/10 l water).
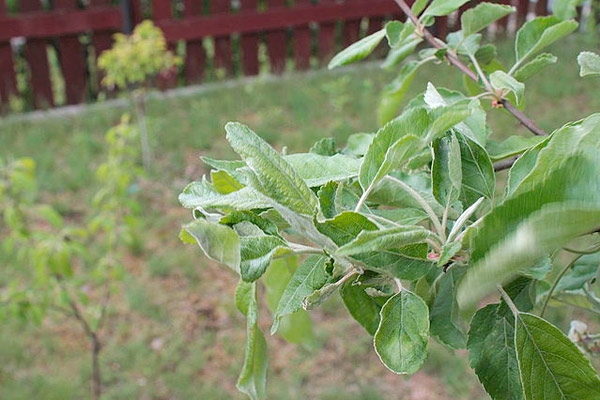

The shoot tips of clonal apple rootstocks intended for planting in mother plantations and first-year nurseries that are infected with powdery mildew are cut off, and heavily infected ones are discarded. All planting material with roots bearing galls caused by bacterial crown gall is also discarded.
Poison baits of boiled maize or wheat grains, Actellic 50 EC; Biona Sincar (4 l per 1 kg grain) and vegetable oil are placed, or Mesurol Schneckenkorn (250 g/da) is buried against mole cricket in seedbeds.
In mother plantations for production of apple rootstocks, shoots infected with powdery mildew are cut back to the base.
In the presence of eggs of San Jose scale, before bud break all trees are sprayed in winter with 3% Acarzin or ParaZomer.
In orchards
March is the deadline for completing machinery repairs. Preparations necessary for control of diseases, pests and weeds during the second quarter are supplied.
If not done in previous months, materials used to wrap the trunks of young fruit trees are collected and burned.
Before bud break, winter spraying of orchards can be carried out, if this was not done in February.
Daily microscopic observations by the Holtz method are made on the maturation of ascospores of the causal agents of apple and pear scab, red leaf spot of plum, fruitlet blight of quince, orange leaf spot of almond, cylindrosporiosis of cherry and other diseases. Spraying against scab is announced as soon as yellowing of ascospores and their discharge after two hours in a moist atmosphere in a Petri dish are established.
Isolation frames are placed over materials collected in the previous year from apple and plum sawflies and cherry fruit fly in order to monitor their development.
On trees heavily infested by the apple leaf miner moth in the previous year, trunk cages are placed to determine the emergence of first-generation moths and the timing of spraying. Protection of apple orchards from this pest depends on timely and high-quality control of the first generation.
The population density of the stone fruit sawfly in cherry and peach plantations is determined by soil excavations. Under 10 trees, two excavations of 50/50/25 cm are made. The same excavations are used to determine the density of the cherry fruit fly in cherry plantations, by sifting the excavated soil through a sieve.
Shoots from 5-10 peach trees are examined to determine the density of the peach twig borer, which overwinters in buds, at the base of one-year growth and in mummified fruits.
If this has not been done in November, 1000-2000 mummified almond fruits are collected from the trees or from the ground. They are placed in cages to monitor the beginning of flight, mass flight and end of flight of the almond seed wasp. The first spraying is carried out after the onset of flight.
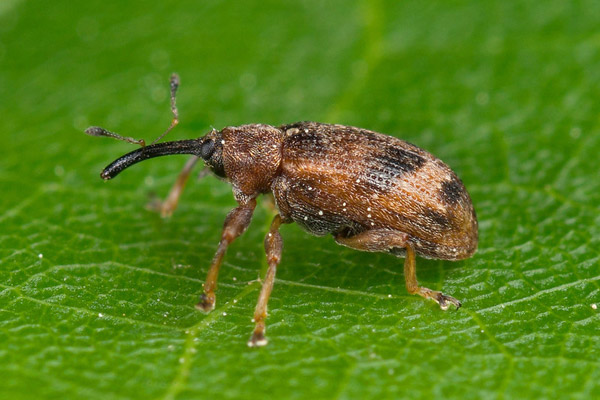

To determine the density of the apple blossom weevil, at the end of the month, beating of branches of 10 apple trees, evenly distributed in the plantation, is carried out. The apple blossom weevil has one generation per year and overwinters as an adult mainly under old and cracked bark of apple and pear trees and to a much lesser extent under fallen leaves. With the warming of the weather, they leave their shelters, feed for some time and then lay their eggs. This period is the most suitable for control of the adult insect.
Shake the branches to check for apple blossom weevil
If more than three beetles per tree are found during branch shaking, spraying is carried out with Sumicidin 5 EC (0.02%), Decis 100 EC (7.5-12.5 ml/da), Deka EC (30-50 ml/da).
The trunks and thick branches of apple trees infested by apple clearwing moth and bark tortrix are sprayed with Coragen 20 SC (16-30 ml/da), Sumicidin 5 EC (0.02%).
Where peach tree buds are in the swelling stage, spraying is done with 1% Bordeaux mixture, Champion 50 WP (300 g/da), Funguran OH 50 WP (150-250 g/da), Capper Key (240-300 g/da) for control of leaf curl, shot-hole disease and brown rot. For shot-hole disease and brown rot, spraying may be carried out up to the pink bud stage.
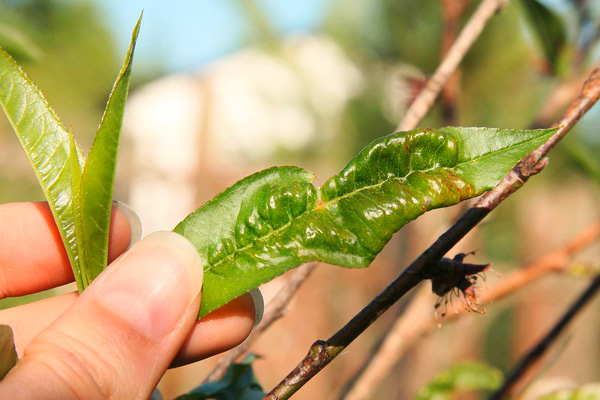

Pre-bloom spraying of apricot, plum and cherry trees is carried out against shot-hole disease – fungal and bacterial – and brown rot, and of almond trees against cercospora leaf spot, shot-hole disease, orange leaf spot and scab with the same preparations. Spraying with Coragen 20 SC (16-30 ml/da), Sumicidin 5 EC (0.02%) against defoliating caterpillars and other pests is also carried out.
According to the signals of the forecasting and warning stations of BFSA, pome fruit trees are sprayed against scab, again with the same preparations and at the same concentrations.
Blossom spraying of apricot trees with Score 250 EC (0.02-0.03%) is carried out against brown rot. Early brown rot is the most dangerous disease of apricot. Copper-containing chemical products must not be used for blossom spraying of apricot!
Soil moisture in March is forecast to be sufficient for uniform germination of weed seeds. On the other hand, it favours the action of soil herbicides, and therefore their application in March is always effective. Only the tree rows of plantations are treated. Before applying herbicides, the soil is loosened and levelled. Herbicides are sprayed with sprayers that are not used for spraying with other pesticides. When this is not possible, after spraying, tanks, pipelines and nozzles of sprayers are thoroughly washed with water in which 2% washing soda or quicklime has been dissolved.
Stomp-Aqua or another herbicide is used in pome and stone fruit species at a rate of 250-300 ml/da.
If drought occurs after herbicide application, sprinkler irrigation is carried out with an irrigation norm not exceeding 30-35 l/m2, since water may wash herbicides into deeper soil layers.
In strawberry plantations
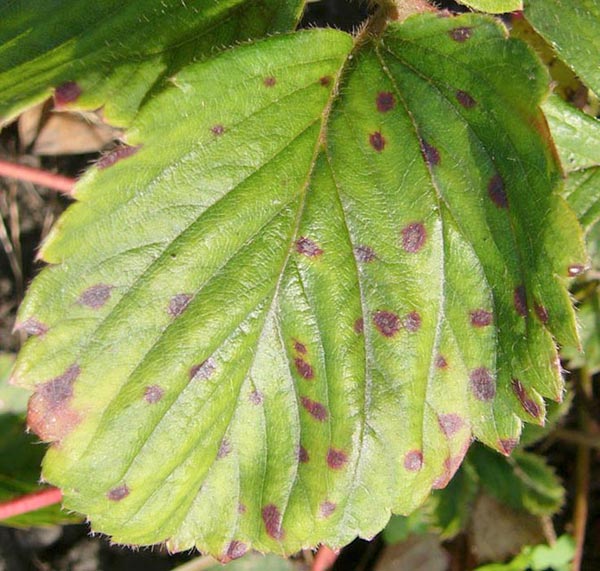

Dried leaves in strawberry plantations are collected and burned in order to destroy the causal agents of white and red leaf spot, powdery mildew, etc.
In raspberry plantations
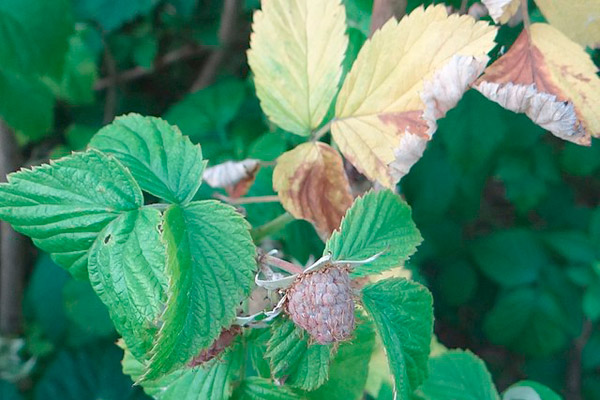

Raspberry canes infested by raspberry moth, didymella, coniothyrium, raspberry gall midge, raspberry clearwing moth and others are cut and burned.
In blackcurrant plantations
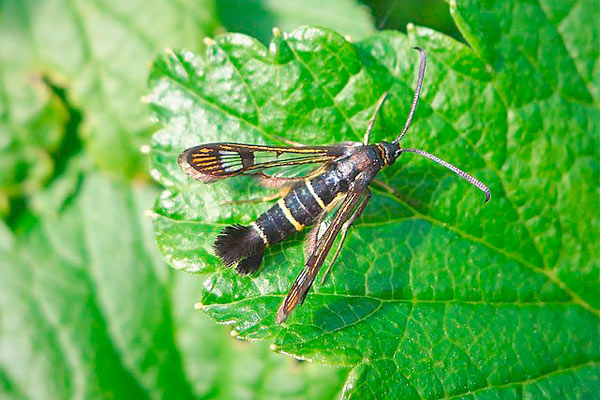

Branches infested by clearwing moth, anthracnose and others are cut without leaving stubs and are burned.

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/заглавна-овощни-март-2024.jpg)

