Plant protection measures for fruit crops in July
Author(s): Растителна защита
Date: 09.07.2022
1946
The relatively dry weather in July allows the fruits of some fruit species and grapevine varieties to ripen within a short period, but also requires that plant protection treatments be carried out during the cooler hours of the day. In addition to spraying with plant protection products, in order to reduce pest density in the orchard, it is of great importance to collect the fallen fruits and remove them from the orchard.
Pome fruit species
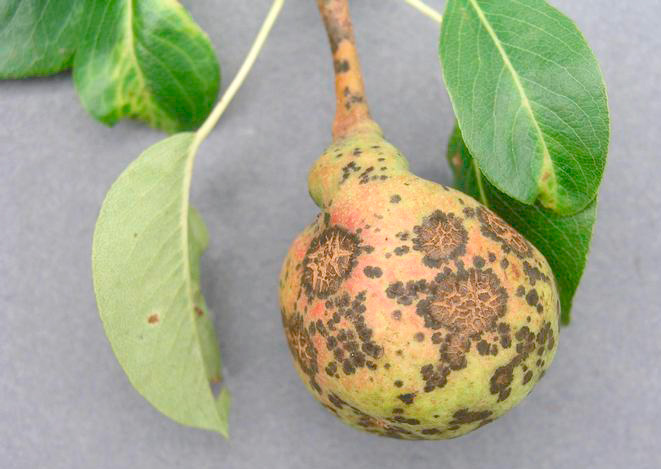

Pear scab
Apple and pear scab
On the formed fruits the spots are irregularly rounded, with a dark coating in the centre and a grey halo at the edges. The spots are often mottled with dark and light zones. Later the coating disappears and corky tissue becomes visible. Severely attacked fruits usually become deformed, crack and often drop prematurely. On fully formed fruits, before ripening, very small, hardly noticeable spots appear, which during storage develop into large scab lesions.
Strategy for pest control
Depending on humidity and the level of infection allowed, treatments are continued until the end of the phenophase “fruit enlargement”.
Biological control
The antagonistic fungi Athelia bom-basika and Chaetomium globosum suppress the formation of ascospores of V. inequalis.
Authorised plant protection products:
Apple
BELIS - 80 g/da; DELAN 700 WG 0.035%; DIFCOR 250 SC - 15 ml/da; LUNA EXPERIENCE - 20-75 ml/da; MERPAN 80 WG – 200 g/da; SULPHUR 544 SC - 125 ml/da; SCORE 250 EC - 0.02%; THIOVIT JET 80 WG - 600 g/da; FABAN - 120 ml/da; FLINT MAX 75 WG - 0.02%; FOLPAN 80 WG - 0.15%; FONTELIS SC - 75 ml/da; CHORUS 50 WG - 0.03% (preventive) 0.05% (curative); CHAMPION WP - 0.3%.
Pear
DIFCOR 250 SC - 15 ml/da; CAPTAN 80 WG - 150-180 g/da; LUNA EXPERIENCE - 20-75 ml/da; POLYRAM DF - 200 g/da; SCAB 80 WG - 188 g/da; THIOVIT JET 80 WG - 600 g/da; FABAN - 120 ml/da; FUNGURAN OH 50 WP - 150-250 g/da; CHAMPION WP - 300 g/da.
Apple powdery mildew
The disease causes russeted threads on the fruits. Infected leaves and shoots appear as if dusted with flour. Attacked leaves become distorted, the tissues beneath the coating turn brown, and more severely affected leaves drop off.
Strategy for pest control
To prevent local infections of powdery mildew, systematic spraying of the trees is necessary.
Authorised plant protection products: BELIS WG - 80 g/da; EMBRELIA - 150 ml/da; SCORE 250 EC - 0.02%; SERCADIS - 15 ml/da; FLINT MAX 75 WG - 0.02%.

Fall webworm
Fall webworm
In July, the moths of the second generation are in flight. The females lay their eggs in clusters on the underside of the leaves, covering them with loose hairs. The caterpillars up to the fifth instar live in common web nests, after which they lead a solitary lifestyle. It is the caterpillars that cause damage – the young ones skeletonise the leaves partially, feeding on the lower epidermis and parenchyma, the older ones perforate the leaves without affecting the veins, and the oldest consume the entire leaf blade.
Strategy for pest control
At low population density, caterpillar nests are cut out and burned. Chemical control is carried out against newly hatched caterpillars, using one of the authorised plant protection products.
Authorised plant protection products: DIPEL 2X – 0.1%, RAPAX - 100-200 g/da

Codling moth
Codling moth
Moths of the second generation of the pest are flying and laying eggs. The caterpillars of this generation destroy the seeds in the seed chamber. Although one fruit is sufficient to feed a single caterpillar, the damage caused by the second generation is significantly higher.
Strategy for pest control
Chemical treatment against the second generation is carried out at the time when the first caterpillars begin to hatch and bore into the fruits. Economic injury level (EIL) for the second generation: 1.5-2% fresh entries in the fruits.
Authorised plant protection product: AFFIRM OPTI - 200 g/da; DECA EC - 30 ml/da; DELEGATE 250 WG - 250 g/da; DECIS 100 EC - 7.5-12.5 ml/da; IMIDAN 50 WG - 150 g/da; SUMI ALFA EC (SUMICIDIN) - 0.02%; SHERPA 100 EW - 300 ml/da; CARPOVIRUSINE - 100 ml/da.
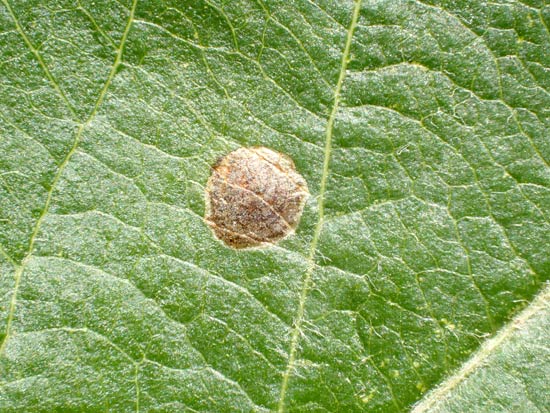

Damage caused by the apple blotch leafminer
Apple blotch leafminer
During the month, development of the second generation is completed and the flight of the moths of the third summer generation begins. With each subsequent generation, the number of mines on the leaves increases. The mines are round, initially tiny like a dot, gradually growing spirally as brown spots. They are clearly visible on both sides of the leaf, especially when viewed against transmitted light. At high population density, two or more mines merge into common patches.
Strategy for pest control
Chemical control is carried out at an EIL: 2-3 eggs and mines per leaf.
Authorised plant protection products: AFFIRM OPTI - 200 g/da; DELEGATE 25 WG - 30 g/da; LAMDEX EXTRA - 60-100 g/da; METEOR - 60-90 ml/100 l water; MOSPILAN 20 SG - 20 g/da; SUMI ALFA 5 EC/SUMICIDIN 5 EC - 0.02%.
California red scale
In July, the second generation of the pest develops. Damage to fruits and leaves by larvae and adult females is of limited economic importance. Small red circular spots appear, with the scale shield visible in the centre. More dangerous are the injuries to the branches and trunks, where anthocyanin spots are observed. As a result of feeding, the branches shrivel and dry out.
Strategy for pest control
Control is aimed at adult males and first-instar crawlers. Treatment is carried out at an EIL: 10 individuals/100 cm of shoot or 2-3 attacked fruits.
Authorised plant protection products: DECA EC / DESHA EC/DENA EC - 50-75 ml/da; METEOR - 90 ml/100 l water; MULIGAN - 30-50 ml/da; OVITEX - 2000 ml/da; BELPROYL-A - 0.375-1.5 l/da; OVIPRON TOP EC – 1000/2000 ml/da (May-August).
Aphids
Aphids suck sap from leaves, shoots and fruits. While feeding they inject secretions that inhibit the growth of the attacked plant parts and hinder their normal development. The damaged organs are strongly deformed, and the fruits remain smaller. In addition to the direct damage from feeding, aphids excrete “honeydew” on the leaves, on which fungal pathogens develop. The contaminated leaf surface prevents normal physiological processes – growth, respiration, transpiration, etc., and the leaves wilt. Later they turn yellow, scorch and fall off.
Strategy for pest control
Spraying is undertaken at an EIL:
Apples and pears
colonies of Aphis spp - 10-15/100 shoots; colonies of Dysaphis spp. - 5/100 shoots.
Authorised plant protection products: DECA EC/DESHA EC/DENA EC - 30-50 ml/da; LAMDEX EXTRA - 40-60 g/da; SHURIDO (former MASAI WP) - 25 g/da; MOVENTO 100 SC - 0.1%; OVITEX - 2000 ml/da; PROTEUS O-TEC - 0.05-0.06%; TEPEKI - 14 g/da.
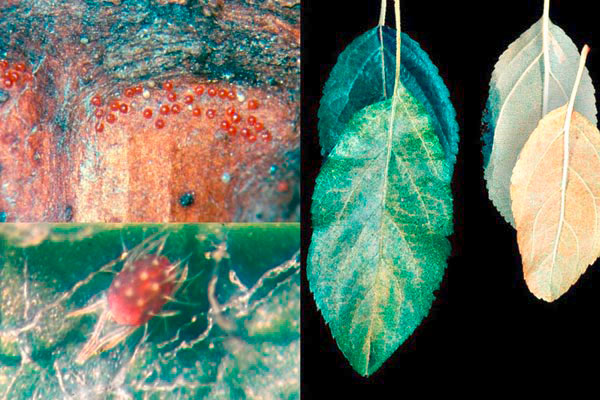
European red mite
European red mite
In dry and warm weather, the population density of the European red mite increases. In summer it develops several generations, as a result of which a large number of pests accumulate on the plants. At very high population density or in competition with other tetranychid mites, the motile forms (larvae, nymphs and adults) of the European red mite may also move to the upper leaf surface and feed there. Under heavy infestation the entire leaves acquire a bronze appearance, then turn yellow and drop prematurely.
Strategy for pest control
Chemical control of infested fruit trees is carried out when the following EIL is reached:
Apple: 3-4 motile forms per leaf.
Pear: 3-4 motile forms per leaf – at the beginning of fruit growth; 5-7 motile forms per leaf – after the beginning of fruit growth.
Authorised plant protection products: APACHE EW - 100 ml/da, VERTIMEX - 100 ml/da, VOLIAM TARGO - 75 ml/da, LAOTA – 60-96 ml/da (apple and pear); SHURIDO (MASAI WP) - 25 g/da, VALMEC - 50-120 ml/da (peach), 37.5-120 ml/da (pear), 60-96 ml/da (apple), VERTIMEC 018 EC - 150 ml/da (apple); OVIPRON TOP EC – 1000/2000 ml/da (May-August).
Stone fruit species
Peach powdery mildew
The disease develops over a wide temperature range, but necessarily under conditions of high air humidity. Prolonged drought, however, does not stop its development. It develops most intensively in the summer months. It affects leaves, fruits and shoots. On the leaves, pale yellowish spots appear, on the underside of which a powdery coating forms. The attacked leaves become strongly deformed and, at high infection pressure, necrotise and fall off. A dense coating also forms on the shoots, causing deformation of the twigs and suppression of their growth. Fruits are infected only early in spring. Spots covered with a dense white powdery coating appear on them. The tissues beneath the coating necrotise and the fruit cracks. Cracked fruits are attacked by rot-causing pathogens and subsequently decay.
Strategy for pest control
Treatment is carried out upon detection of the first spots. Thereafter, spraying is done at intervals of 10 to 12 days until the end of the phenophase “fruit sizing”.
Authorised plant protection products: LUNA EXPERIENCE - 50 ml/da, SCORE 250 EC - 20-30 ml/da, SIGNUM - 30 g/da, SISTAN 20 EW - 30 ml/da, THIOVIT JET 80 WG - 600 g/da, TOPAZ 100 EC - 0.03%.

Late brown rot on plum
Late brown rot
On attacked fruits a small, round, brown spot appears, which gradually enlarges and covers the entire fruit. Later, large sporulating tufts of yellowish-white colour appear on the browned and rotten tissues, arranged in concentric rings. The attacked fruits either drop prematurely or remain mummified on the branches.
Strategy for pest control
Under favourable conditions for disease development and upon appearance of the first symptoms, treatments are carried out with authorised plant protection products. The pre-harvest intervals of the fungicides used must be observed.
Authorised plant protection products: CAPTAN 80 WG - 150-180 g/da, LUNA EXPERIENCE - 63-75 ml/da, PROLECTUS 50 WG - 120 g/da, SIGNUM WG - 60-75 g/da, CHORUS 50 WG - 0.045%, MERPAN 80 WG - 225 g/da, PASSWORD 25 WG - 50 g/da.
White leaf spot (Cylindrosporiosis) on sweet and sour cherry
The most typical symptoms of the disease are on the leaves – small, purplish-red spots. The spots appear in cool and wet weather and can cover the entire leaf blade. On the underside of the leaves a characteristic whitish coating forms, consisting of the sporulation of the fungus in the form of small tufts. Unlike shot-hole disease, the tissue within the spots does not fall out. Under heavy infection, white leaf spot causes massive leaf drop, leading to defoliation of the trees.
Strategy for pest control
After completion of harvest, including late cultivars of sweet and sour cherries, and under severe disease infestation, two consecutive sprays are carried out at 10-12 day intervals with one of the authorised fungicides.
Authorised plant protection products: DELAN 700 WG – 0.05%; SIGNUM – 0.03%; SULPHUR 544 SC – 125 ml/da; SCORE 250 EC – 0.03%; FLINT MAX 75 WG – 30 g/da; AZAKA - 100 ml/da.

Plum rust
Plum rust
On the upper leaf surface numerous small, angular, yellow or reddish spots are observed. On the underside, the spots are covered with dusty spore heaps. Severely infected leaves turn yellow and drop prematurely. In heavily affected trees, fruits ripen prematurely, remain small and with reduced sugar content, and the trees themselves become highly susceptible to winter injury.
Strategy for pest control
Treatment is carried out upon appearance of the first spots on the leaves. Under severe infection, one or two additional sprays are applied at twenty-day intervals.
Authorised plant protection product: SIGNUM WG - 45 g/da
Plum fruit moth
During the month, the flight, egg laying, hatching and damaging activity of the caterpillars of the second generation of the pest continue. The newly hatched caterpillar bores into the fruit close to the oviposition site. Around the stone, in the fleshy part of the fruit, it excavates a gallery filled with excreta and frass. The damaged fruits show signs of premature ripening and drop off.
Strategy for pest control
Chemical treatment is carried out at an EIL for the second generation: 1.5-2% fresh entries in the fruits;
Authorised plant protection products: AFFIRM OPTI - 250 g/da, DECA EC 50-70 ml/da, DELEGATE 250 WG - 300 g/da, DECIS 100 EC - 7.5-17.5 ml/da, IMIDAN 50 WG - 150 g/da, CORAGEN 20 SC, VOLIAM - 16-30 ml/da, CORAGEN 20 SC - 16-30 ml/da, SUMI ALFA 5 EC - 0.02%.

Oriental fruit moth
Oriental fruit moth
In July, moths of the second generation of the pest are flying and laying eggs. The caterpillars of the third generation damage mainly the fruits. The caterpillar bores laterally, at the points of contact between the fruits or near the stem. Gum exudation is often observed. Damaged fruits become deformed or rot. They show signs of premature ripening and drop off.
Strategy for pest control
Chemical control is carried out at an EIL:
during the vegetation – 10-15 moths/trap/week;
young orchards – 2-3% attacked shoots by the caterpillar;
fruit-bearing orchards - 5% damaged shoots or 2-4% attacked fruits by the caterpillar.
Authorised plant protection products: AVANT 150 EC - 33.3 ml/da, AFFIRM OPTI - 200 g/da, VOLIAM TARGO - 75 ml/da, DECA EC - 50-70 ml/da, DELEGATE 250 WG - 30 g/da, DIPEL DF - 75-150 g/da, LAMDEX EXTRA - 70 g/da, CORAGEN 20 SC, VOLIAM - 16-30 ml/da, CORAGEN 20 SC - 16-30 ml/da, SUMI ALFA 5 EC - 0.02%, MADEX TWIN - 10 ml/da,
CARPOVIRUSINE - 100 ml/da.

Peach twig borer
Peach twig borer
In July, the second generation of the pest develops. The caterpillars of this generation damage both shoots and fruits. Attacked shoots wilt, their terminal part dries together with the leaves, and growth stops. On the fruits, the caterpillars bore a short gallery in the fleshy part. The damage resembles that caused by fruit moths.
Strategy for pest control
Treatment is carried out at an EIL - 3% damaged fruits by caterpillars.
Authorised plant protection products: AFFIRM OPTI - 200-225 g/da;
VOLIAM TARGO 063 SC – 75 ml/da; DECIS 100 EC - 8.75–12.25 ml/da; DIPEL DF - 75-150 g/da, CORAGEN 20 SC - 16–30 ml/da; AVANT 150 EC - 33.3 ml/da; RAPAX – 100–200 ml/da; SYNEIS 480 SC – 20 ml/da.

The false caterpillar of the cherry slug sawfly is yellow-green. The body is covered dorsally with a black slimy substance that masks its basic colour.
Cherry slug sawfly
Throughout July, the second generation of the pest develops. Damage is caused by the larvae, which scrape the upper epidermis and feed on the parenchyma of the leaves. The lower epidermis remains intact and is scorched by the sun. Damaged leaves turn yellow, then brown and fall off.
Strategy for pest control
At high population density, treatment is directed against the adults before egg laying and against the false caterpillars immediately after hatching.
Authorised plant protection products: DECA EC - 30 ml/da.

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/градина-юли-2022.jpg)

