Physiological changes caused by excess phosphorus
Author(s): доц. д-р Венета Каназирска
Date: 10.04.2022
2118
PHOSPHORUS (P – Phosphorus from the Greek „Φωσφόρος” – light)
General symptoms
It is observed more frequently in hydroponic crops than in soil-grown ones. The reason is that in vegetable crops grown in soil, on the one hand, phosphorus in the soil passes into sparingly soluble compounds, and on the other hand – these crops extract significant amounts of P2O5 – celery 90 kg/ha, tomatoes 81 kg/ha, potatoes 73 kg/ha. The main symptom of excess phosphorus is growth retardation. Symptoms of deficiency of copper, zinc, iron, cobalt, and calcium develop.
Cause
High level of plant-available phosphorus in the soil. The effect is enhanced at a high level of nitrate nitrogen.
Recommendation
Foliar fertilization with a solution of fertilizers containing micronutrients (zinc, copper, iron, cobalt).
Identification of symptoms of excess phosphorus by crops

Excess phosphorus in fruit vegetable crops
Symptoms of excess phosphorus in fruit vegetable crops:
- The older leaves are light yellow, while the younger leaves remain dark green, but later they also turn yellow, first between the veins and then – entirely. Bright necrotic spots appear and the leaves fall off;
- The formation of reproductive organs is inhibited.
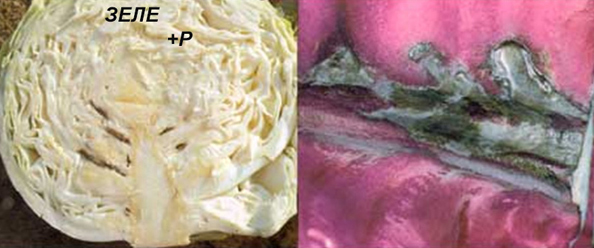
Excess phosphorus in leafy-stem vegetable crops
Symptoms of excess phosphorus in leafy-stem vegetable crops:
- When the heads approach maturity, the midrib of the inner leaves becomes dark grey or brown. The effect is enhanced at a low level of potassium or a high level of nitrogen in the nutrient medium.

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/tomato-diagnostik-излишък-фосфор.jpg)

