Physiological changes caused by excess nitrogen
Author(s): доц. д-р Венета Каназирска
Date: 03.04.2022
4366
NITROGEN (N – Nitrogen)
Excess nitrogen
General symptoms
Excessive and unbalanced nitrogen fertilization affects plant growth and productivity adversely. Growth is enhanced, leaves grow vigorously, become dark green and their senescence is delayed. The vegetation period is prolonged and ripening is delayed. Excess nitrogen is particularly harmful in fruit, root and tuber vegetable crops, since a lush vegetative mass is formed at the expense of fruits, roots and/or tubers.
Large amounts of organic nitrogen compounds, especially proteins, accumulate in the plant organism. Due to the accumulation of proteins, which are highly hydrophilic, plant tissues become soft and succulent, which makes them more susceptible to fungal diseases and insect attacks.
In most crops the quality of the produce decreases significantly – both in appearance and in organoleptic properties.
In the case of a large excess of nitrogen in the nutrient medium, symptoms of potassium and/or copper deficiency appear. In the case of a very high nitrogen excess the roots “burn”, growth is suppressed and plants wilt under high solar radiation. In ammonium nitrogen (N-NH4) toxicity, the margins of young leaves become brown and then necrotic, and growth is inhibited.
Causes
Elevated nitrogen content and/or high potassium content in the nutrient medium.
Recommendations
Leaching of the soil or substrate (this practice is effective with good drainage); reduction of transpiration; foliar fertilization with a 0.1% solution of copper sulfate, neutralized with lime.

Excess nitrogen in fruit vegetable crops
A – ammonium nitrogen toxicity (NH4-N)
Identification of symptoms of excess nitrogen by crop
Symptoms of excess nitrogen in fruit vegetable crops:
- A large leaf mass is formed. The leaves become dark green with a boat-shaped form (tomato, pepper, eggplant), crisp when squeezed and with scorch at the tips and margins;
- In ammonium nitrogen (N-NH4) toxicity, the margins of young leaves become brown and then necrotic. Necrotic spots appear on the stem;
- The number of flowers and fruits decreases. Their quality deteriorates;
- In the case of a very high nitrogen excess the roots “burn”, growth is suppressed and plants wilt under high solar radiation. Symptoms of copper deficiency appear.
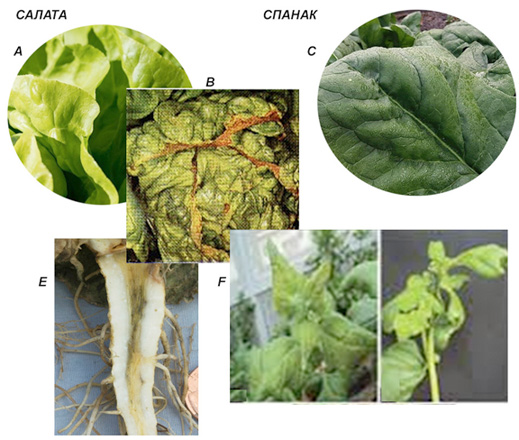
Excess nitrogen in leafy vegetable crops – the first phase is vigorous vegetative growth (A, C), followed by scorch formation (B); E, F ammonium (NH4-N) toxicity
Symptoms of excess nitrogen in leafy vegetable crops:
- A lush vegetative mass develops, followed by scorch along the leaf margins;
- In excess ammonium nitrogen (NH4-N) growth stops. The reason is that the root system is severely affected. The root becomes yellow or light brown and cracks are formed (the symptoms resemble root corking – corky root), and the central core becomes yellow to light brown, later shrinks and a cavity is formed along the length of the root.
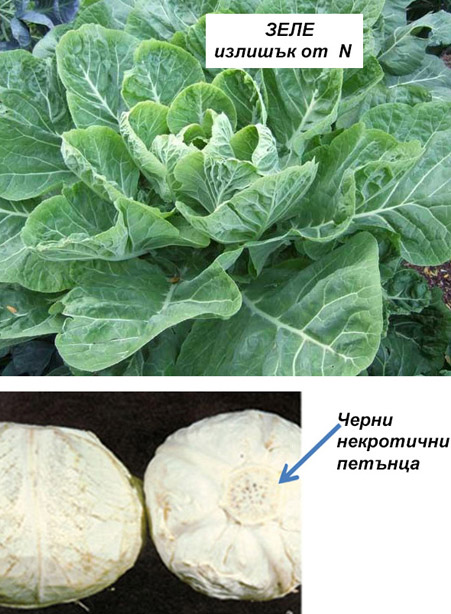

Excess nitrogen in leafy-stem vegetable crops
Symptoms of excess nitrogen in leafy-stem vegetable crops:
- The vegetative mass develops vigorously, while the root system is weaker. This creates problems with transpiration;
- Head formation is delayed or small heads develop;
- Small black necrotic spots appear on the outer leaves of the head, which often spread inwards. Symptoms intensify during storage under cool conditions.
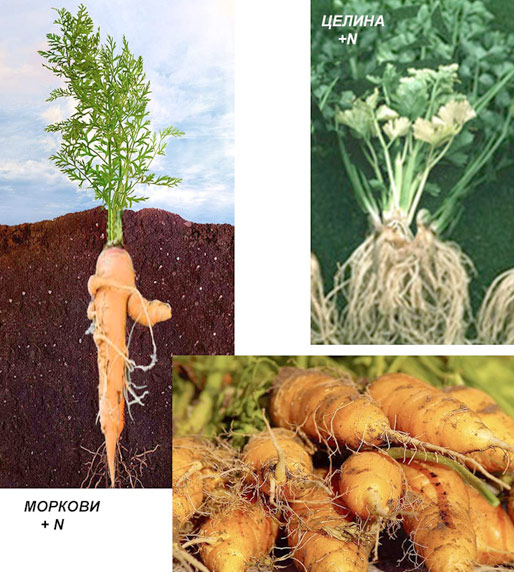

Excess nitrogen in root vegetable crops
Symptoms of excess nitrogen in root vegetable crops:
- A rich dark green leaf mass is formed at the expense of the root;
- The quality of the produce is impaired – roots are “hairy” with many small rootlets and no main root.
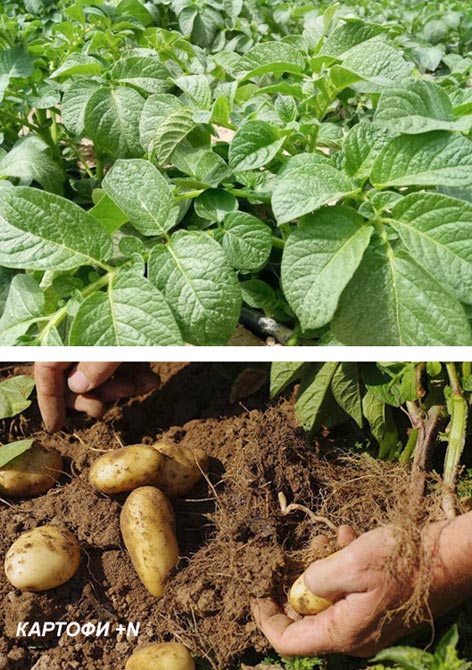

Excess nitrogen in tuber vegetable crops
Symptoms of excess nitrogen in tuber vegetable crops:
- A rich dark green leaf mass is formed;
- Fibrous roots are formed, while the number and mass of tubers decrease;
- The nutritional value of the produce deteriorates – the content of vitamin C decreases;
- The quality of potatoes for frying deteriorates (they disintegrate).

![MultipartFile resource [file_data]](/assets/img/articles/tomato-diagnostik-излишък-azot.jpg)

